15
Diagnostic Manual
SEVENSTEPSDIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
4
(e.g. Horn/Music System/Woofers/Lighting/
Central locking/Others(Specify))
8. Has any repair been done in wiring harness?
(e.g. Engine/Cabin/Floor/Interconnection etc.)
Step 2 - Replicating the Concern
The Service advisor needs to replicate the con-
cern by exactly recreating the conditions of the
complaint’s occurrence. This will help to gather
additional information about the concern.
For a better understanding of the concern, simu-
late the conditions of its occurrence, as closely
as possible for e.g.
•
If complaint occurs in high speeds, test it on
highway.
•
If complaint occurs when clutch is pressed,
press the clutch and check.
•
If complaints occur when vehicle is being driven
in bumper to bumper traffic condition, test it in
high traffic area.
•
If complaint occurs when AC kept ‘ON’, test it
with AC ‘ON’
•
If complaint occurs when engine is hot, keep
the engine started for sometime and check.
•
Many of the understanding gaps get cleared
between the ServiceAdvisor and the customer
during this stage.
Step 3 - Analyzing the Symptoms
This step starts after having a complete under-
standing of the customer’s concern. This is basi-
cally the information gathering stage by checking
the specific ECU’s parameters and values and
comparing them with what it should be.
Condition 1: Permanent DTCs Present
•
Connect the TML diagnostic tool to the
vehicle.
•
Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC’s)
& their status.
•
Record the DTC & Clear
•
Turn Ignition OFF & ON
•
If any permanent DTC is present, follow the trou-
bleshooting data provided against every DTC
in diagnostic tool.
•
Check for appropriate checklists, service
circulars and workshop manual as per the
DTC’s or Symptom for more information.
Condition 2: Intermittent DTCs Present
Perform the following checks for intermittent
problems:
•
Battery cable for proper tightening on battery
posts.
•
Voltage drop due to loose earthing joints in ve-
hicle.
•
Oxidation/Corrosion on cable clamps or wire
terminals.
•
Locking of the mating connector
•
Primary & Secondary lock in connector
•
Loose/flare & back out terminals in the con-
nector
•
Temporary short between wires.
•
Improper Crimping of terminal or wire joints.
Condition 3: Cases where no DTC is Present
Perform a thorough visual inspection and
compare the engine parameters with known
good vehicle under the same conditions based
on Symptoms:
•
Check for obvious problems based on
Symptom (basics, basics, basics).
•
Check the battery voltage.
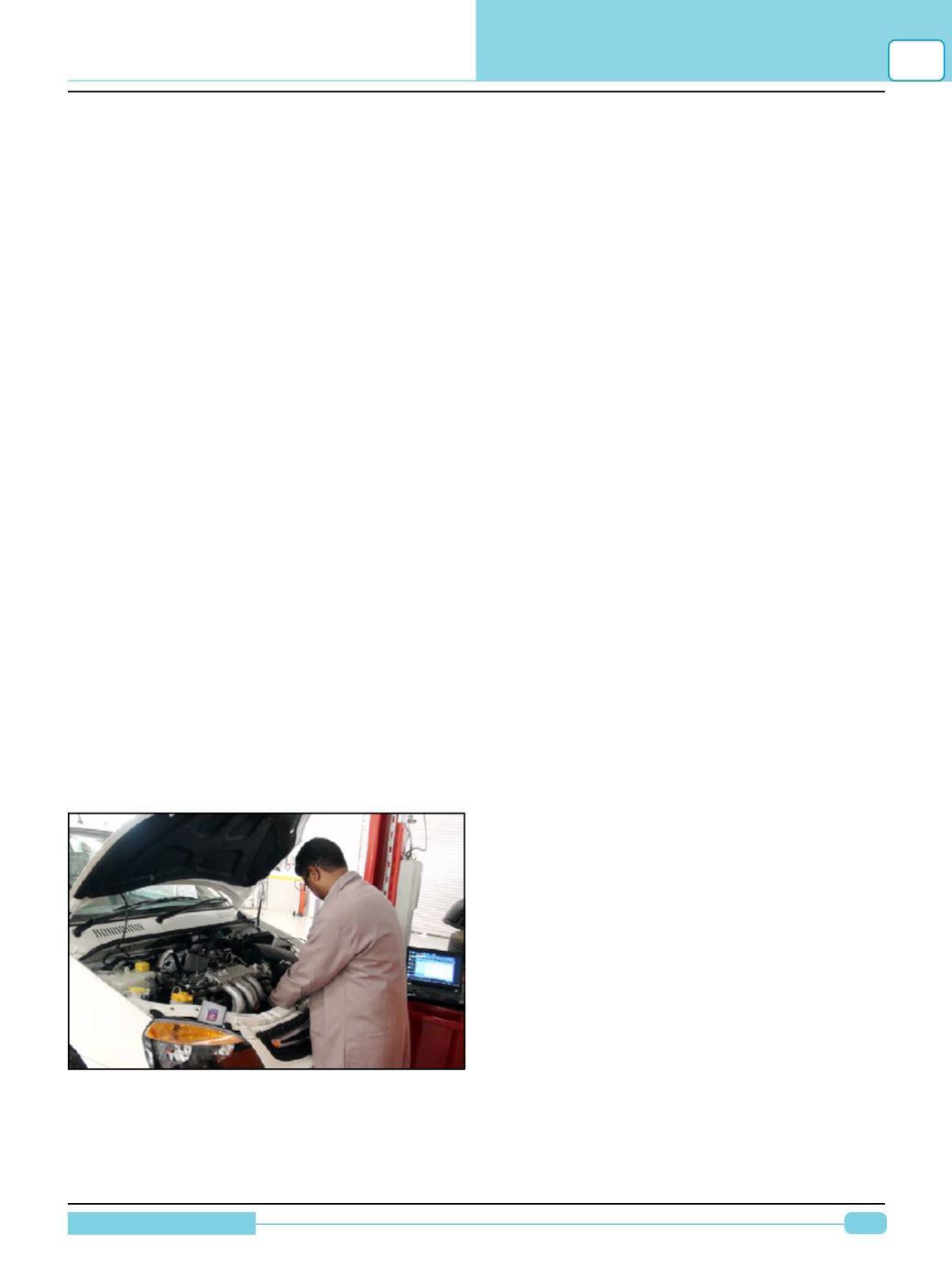
FIG.2 : After checking for stored diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC’s), the wise technician
checks service information for any techni-
cal service bulletins that may relate to the
vehicle being serviced.